Impetigo: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment – and How it Differs from Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Impetigo is a common and contagious bacterial skin infection. It typically affects children between two and five years old, but anyone can get it.
Keep reading to learn basic facts about impetigo, prevention tips, treatment options, and how it differs from hand, foot, and mouth disease.
What causes impetigo?
Impetigo is an itchy, sometimes painful, skin infection. It starts with a break in the skin from a cut, insect bite, scratch, or skin damage from eczema. The open wound allows bacteria to move in and cause an infection. The infection is caused by bacteria, including group A streptococcus (strep) and staphylococcus aureus (staph). Impetigo occurs more often in warmer months when children are outside.
What are the signs and symptoms of impetigo?
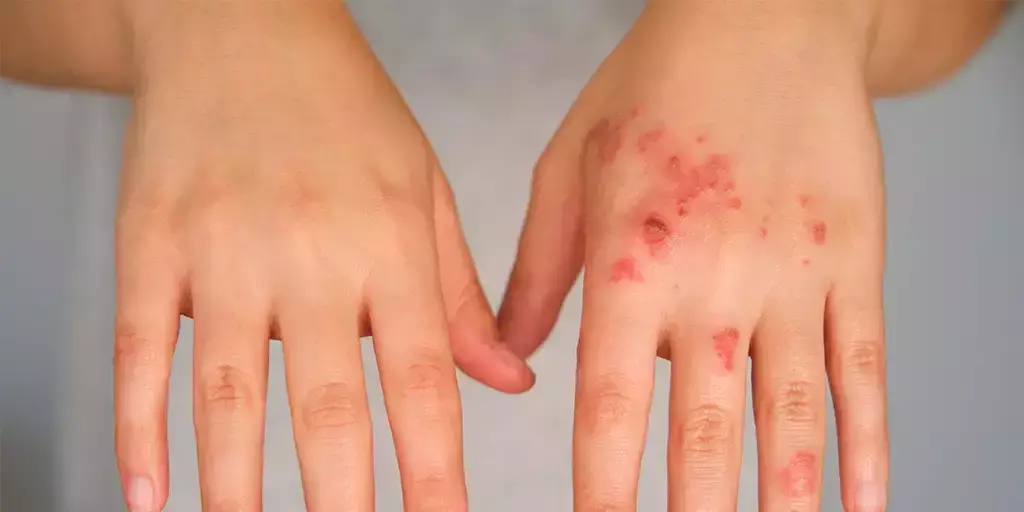
Symptoms of impetigo develop within three days after the bacteria infects the skin. The first signs are red itchy sores that break open and leak pus or a clear fluid for several days. Next, a crusty yellow-brown scab forms over the sore, which typically heals without leaving a scar. Impetigo most often affects exposed skin – around the mouth and nose and on the arms and legs. It can also appear on the scalp or hairline.
Untreated, impetigo can develop into ecthyma, which is more serious and goes deeper into a child’s skin.
Is impetigo contagious?
Impetigo is highly contagious. Most people get it through direct skin-to-skin contact. You can also get impetigo by coming into contact with sores, mucus, or nasal discharge from someone who has it. Children and athletes often get it this way.
Sharing towels, clothing, or personal items with an infected person is another way impetigo spreads.
Without treatment, impetigo can be contagious for weeks.
How is impetigo diagnosed?
A healthcare provider can diagnose impetigo based on how the sores look. They may also take a sample and send it to a lab, which can help your provider determine the best treatment.
How do you treat impetigo?
Your healthcare provider will prescribe antibiotics to treat impetigo. Topical antibiotics are applied to the affected area if it’s small. Oral antibiotics are used for cases where a large area is affected. Once an antibiotic is started, healing begins within a few days, but it’s essential to complete the entire course of antibiotics even after the infection improves.
Clean the infected area daily with soap and water to gently remove the scabs and yellow crusts. The open sores should be covered loosely with a bandage to prevent the infection from spreading to others.
After starting treatment, the condition is contagious until the rash disappears, scabs fall off, and you’ve been on antibiotics for at least two days.
How can you prevent getting impetigo?
The best way to avoid getting this bacterial infection is to prevent breaks in the skin. If a break develops, clean it with soap and water and apply an over-the-counter antibiotic cream or until it heals. Avoid picking at sores or scabs to keep bacteria out. Also, never share towels or washcloths with someone with an active skin infection.
How can you avoid spreading impetigo?
Since impetigo is highly contagious, avoid close contact with anyone until the rash is clear or improving after two days of antibiotics. If you come in contact with the infection, wash your hands and the exposed skin thoroughly with soap and water. Also, towels and washcloths should be kept separate from those of other family members.
How is impetigo different than hand, foot, and mouth disease?
Although these infections share similar symptoms, they are two different conditions.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a highly contagious viral infection that usually affects young children. The most common symptoms are fever, mouth sores, and a rash on the hands and feet. HFMD is usually mild and resolves on its own within a week or two.
Read More: Integrity Urgent Care Health Handbook – Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Impetigo is a contagious bacterial skin infection that can affect people of all ages. The most common symptom is a crusty, pus-filled blister. Impetigo will worsen if it’s not treated with antibiotics.
Integrity Urgent Care Can Help
If you suspect you or your child might have impetigo, it’s vital to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Find an Integrity Urgent Care location near you to prevent the spread of this highly contagious infection. We provide quality, affordable care for non-life-threatening injuries and illnesses. Integrity Urgent Care, part of the Xpress Wellness family, is a Texas-based walk-in clinic with over 15 convenient locations. Walk in, check-in online, or consider a virtual healthcare visit.
Read More: Virtual Visits with Integrity Urgent Care: Healthcare from the Comfort of Your Home